The Next Generation Africa Call for Startups received 326 applications from startups across the continent. This initiative was launched to support African early-stage startups and provide them with the resources they need to grow and scale their businesses, creating networking opportunities with the Italian innovation ecosystem.
Here are some insights and takeaways from the call for startups:
1. Team Size
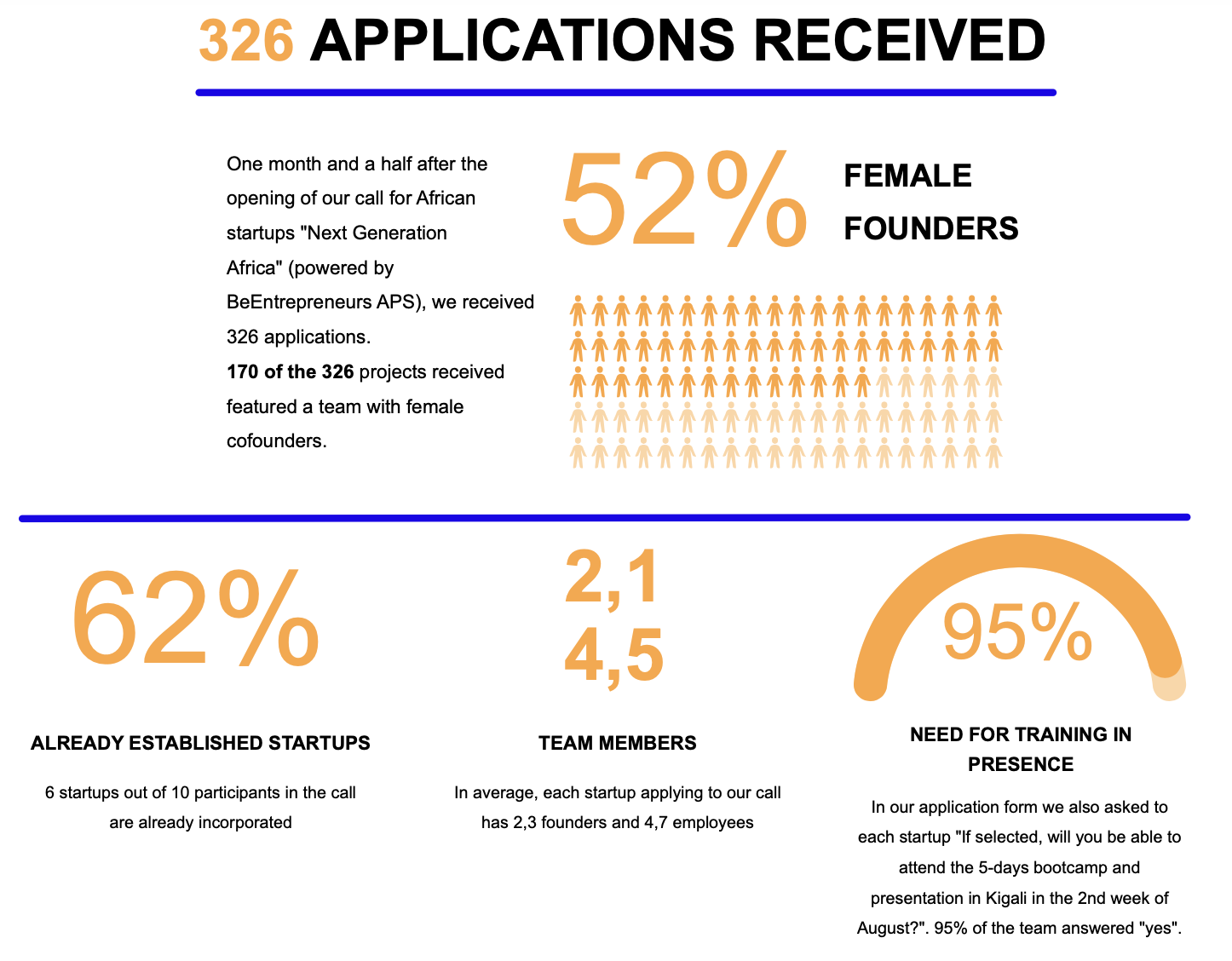
On average, each startup that applied to the call had 2.3 founders and 4.7 employees. This indicates that most startups in Africa are small teams, with a focus on lean operations and efficiency. However, there were some startups that had larger teams, with up to 20 employees.
2. Gender diversity
170 of the 326 projects received featured a team with female co-founders. This is a positive sign for gender diversity in the startup ecosystem and shows that women are taking an active role in shaping the future of African entrepreneurship. However, there is still work to be done to ensure that women have equal access to resources and opportunities in the startup ecosystem.
3. Established Startups
62% of the participating startups were already incorporated. This indicates that there is a growing number of startups in Africa that are gaining traction and making an impact in their respective industries. However, there is still a need to support early-stage startups, as they are the ones that are most in need of resources and support.
4. Geographic Distribution
The startups that applied to the call came from 36 different countries across Africa.
The majority of the startups that applied to the call were from East Africa, with 90.1% of the applications coming from this region.
The top countries represented were:
1. Rwanda: The highest number of startups that applied to the call were from Rwanda, with 27% of the applications coming from this country.
2. Uganda: The second-highest number of startups that applied to the call were from Uganda, with 19.6% of the applications coming from this country.
3. Kenya: 15.9% of the applications came from Kenya.
4. Tanzania and Nigeria: 7,4% of the applications came from Tanzania and Nigeria.
5. Democratic Republic of the Congo: 2.7% of the applications came from the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
6. United States: 2.7% of the applications came from the United States.
7. Ghana: 1.8% of the applications came from Ghana.
8. Other: 14.4% of the applications came from other countries, including Burundi, Ethiopia, Senegal, South Africa, Zambia, Botswana, and more.


5. Industry Breakdown
The startups that applied to the Next Generation Africa Call for Startups came from a variety of industries. The breakdown of the industries represented in the call for startups:
– Agribusiness / Circular economy (26.1%)
– ICT (17.8%)
– Edtech & HR (13.5%)
– Healthcare (12.8%)
– Sustainable energy & mobility (7.1%)
– Fintech (7.9%)
– Travel & Hospitality (6.7%)
– Manufacturing (7.9%)
This breakdown shows that there is a diverse range of startups in Africa, with a focus on industries that have the potential to make a significant impact on the continent.

– Agribusiness / Circular economy: This sector had the highest representation in the call for startups, with 85 startups applying. This is also not surprising, given that agriculture is a key industry in Africa. The agriculture startups that applied to the call were focused on a variety of areas, including agribusiness, food processing, and more. The focus of these startups was on agribusiness and circular economy, which involves creating a closed-loop system where waste is minimized and resources are reused.
– ICT: 58 startups applied from the ICT sector, which includes startups focused on information and communication technology. These startups were focused on a variety of areas, including mobile apps, software development, and more.
– Edtech & HR: 44 startups applied from the edtech and HR sector, which includes startups focused on education technology and human resources. These startups were focused on a variety of areas, including e-learning, skills development, and more.
– Healthcare: 42 startups applied from the healthcare sector, which includes startups focused on healthcare technology and services. This is a positive sign, as healthcare is an important industry that has the potential to make a significant impact on the continent. The healthcare startups that applied to the call were focused on a variety of areas, including telemedicine, medical devices, and more.
– Sustainable energy & mobility: 23 startups applied from the sustainable energy and mobility sector, which includes startups focused on renewable energy and transportation. These startups were focused on a variety of areas, including solar energy, electric vehicles, and more.
– Fintech: 26 startups applied from the fintech sector, which includes startups focused on financial technology. This is not a surprising trend, given the growing interest in financial technology in Africa. Fintech has the potential to make a significant impact on the continent, by providing access to financial services to those who were previously excluded from the traditional banking system. The fintech startups that applied to the call were focused on a variety of areas, including mobile payments, remittances, lending, and more.
– Travel & Hospitality: 22 startups applied from the travel and hospitality sector, which includes startups focused on tourism and hospitality. These startups were focused on a variety of areas, including travel booking platforms, hotel management software, and more.
– Manufacturing: 26 startups applied from the manufacturing sector, which includes startups focused on manufacturing and production. These startups were focused on a variety of areas, including 3D printing, food processing, and more.
6. Commitment to Learning
95% of the teams that applied said they would be able to attend the 5-day bootcamp and presentation in Kigali in the 2nd week of August. This is a strong indication of the commitment and dedication of African startups to take advantage of opportunities to learn and grow. This commitment to learning is essential for startups to succeed in a rapidly changing business environment.
7. Collaboration and Networking
The selected startups will have the opportunity to participate in a 5-day bootcamp and presentation in Kigali, Rwanda. This is a chance to network with other startups, meet investors, and gain valuable insights from industry experts. Collaboration and networking are essential for startups to succeed, as they provide access to resources and opportunities that would otherwise be unavailable.
Speaking about this first phase of “Next Generation Africa” initiative, Andrea Censoni, President & Co-founder at BeEntrepreneurs said:
Overall, Next Generation Africa Call for Startups shows that there is a growing interest in entrepreneurship in East Africa, with a focus on industries that have the potential to make a significant impact on the continent. We are excited to see what the future holds for these startups and we believe that they have the potential to make a significant impact in their respective industries and communities.
Stay tuned on our social media channels to find out the next phases and the selected projects!
Click here for more information about “Next Generation Africa”.





















Recent Comments